📌 Overview
🎯Learning Objectives
- Linearity, superposition ✅ 2025-09-28
- Source Transformation ✅ 2025-09-28
- Thévenin and Norton Theorems ✅ 2025-09-28
- Maximum power transfer ✅ 2025-09-28
💡Key Concepts & Definitions
➗ Formulas
✍️ Notes
Superposition
- CAN be applied to currents and voltages
- CANNOT be applied to powers
- Take one source, turn all other off
- modify sources
- Replace voltage sources by short circuits
- Replace current sources by open circuits

- Evaluate the requested voltages / currents
- Add all partial results
Source transformation
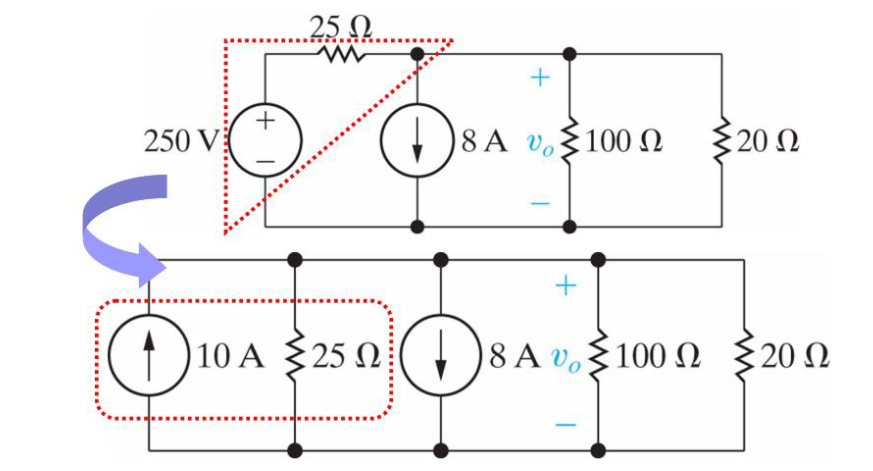
Using source transformation can simplify calculation
Voltage source and resistor can be replace by current source with parallel resistor
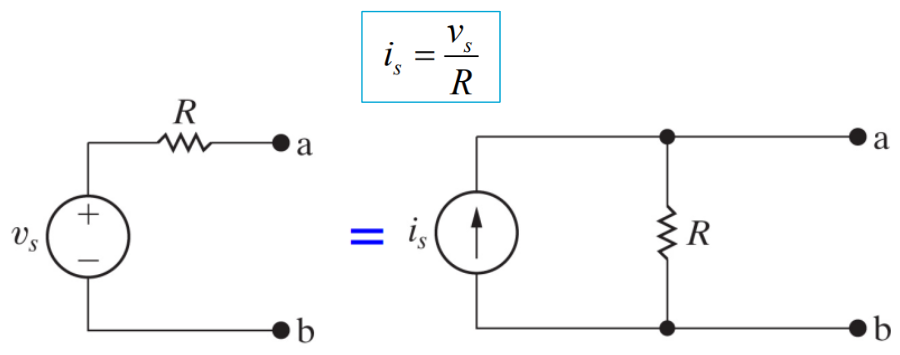
When calculating certain value, not all resistors are relevant
- For Voltage Source: All parallel resistors to target
- For Current source: All resistors in series
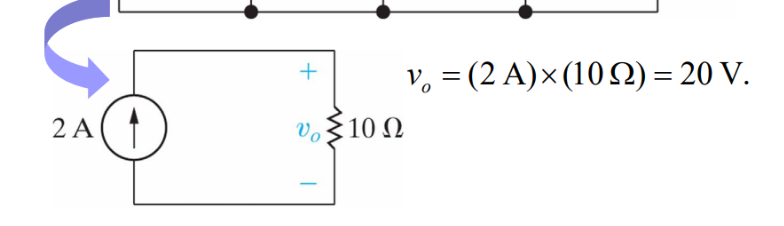
Thévenin & Norton Theorems
-
Goal: Simplify calculation
-
The original linear circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit consisting of one independent source in series with one equivalent resistance
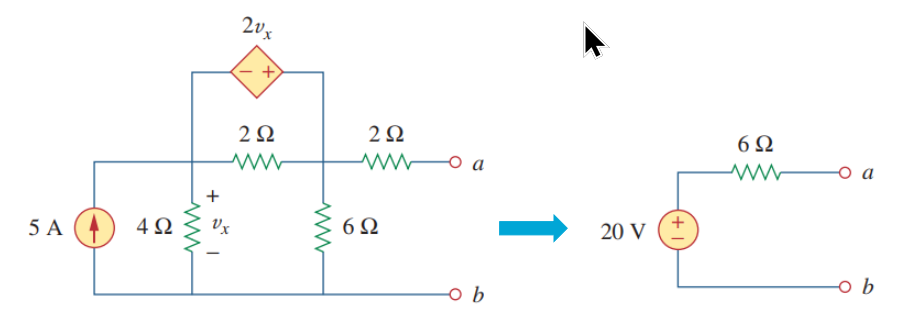
- with independent sources, only
- determine Voc or Isc; determine RTh
- with dependent sources, only
- Voc and Isc = 0; determine only RTh by connecting a “test-source”
- both independent and dependent sources
- a bit more work
Steps:
- Remove the load resistor (R_L) to create an open circuit between terminals A and B.
- Calculate the open-circuit voltage (V_oc) across terminals A and B. This voltage is the Thévenin equivalent voltage (V_Th).
- Deactivate all independent sources. This means replacing voltage sources with short circuits and current sources with open circuits.
- Calculate the equivalent resistance (R_Th) looking back into the circuit from terminals A and B.
- Draw the Thévenin equivalent circuit: A voltage source V_Th in series with the resistor R_Th.
- Reconnect the load resistor (R_L) to the terminals of the equivalent circuit and easily calculate the voltage across it using the voltage divider rule.
Maximum power transfer
🔗 Resources
- Presentation: